1. FIFO(First In First Out) - 큐의 자료 구조
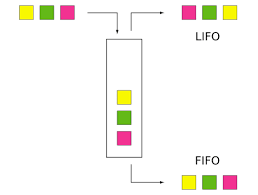
선입선출. 먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나간다.
대기열 등에서 쓰임.
2. 문법
(1) 데이터 삽입 ; push
int main()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);(2) 가장 앞에 있는 원소 추출 ; front, 데이터 삭제 ; pop
int data = q.front();
q.pop();(3) 원소 개수 ; size
int size = q.size();(4) 모든 데이터 추출하기 ; empty
while (q.empty() == false)
{
int data = q.top();
q.pop();
}
3. 구현
동적배열(vector)로 구현하려고 하면 일부 기능이 지원되지 않는다.
(push_front, pop_front 등)
따라서 이중 연결 리스트(list)로 구현한다.
template<typename T>
class Queue
{
public:
void push(const T& value)
{
_container.push_back(value);
}
void pop()
{
_container.pop_front();
}
T& front()
{
return _container.front();
}
bool empty() { return _container.empty(); }
int size() { return _container.size(); }
public:
list<T> _container;
};기본적으로 queue는 deque를 사용하여 구현되어있다.
4. 배열 기반, 순환 구조로 큐 구현하기
처음에 데이터가 없을 때는 front와 back이 첫 인덱스에 있다.
이후에 데이터가 늘어날 때마다 front와 back 사이에 저장된다.
[front, back] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[front] [data1] [back] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
[front] [data1] [data2] [back] [ ] [ ] [ ]
그리고 front부터 back 까지의 데이터가 유효 데이터이다.
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ back ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ front ] [ ] [ ]
template<typename T>
class ArrayQueue
{
public:
ArrayQueue()
{
_container.resize(100);
}
void push(const T& value)
{
//큐가 다 찼는지 체크 후 증설
if (_size == _container.size())
{
int newSize = max(1, _size * 2); // 둘 중에 더 큰 값을 리턴
vector<T> newData;
newData.resize(newSize);
// 데이터 복사
for (int i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
int index = (_front + i) % _container.size();
newData[i] = _container[index];
}
_container.swap(newData);
_front = 0;
_back = _size;
}
_container[_back] = value;
_back = (_back + 1) % _container.size(); // 순환 구조
_size++; // 유효 데이터 개수
}
void pop()
{
_front = (_front + 1) % _container.size();
_size--;
}
T& front()
{
return _container[_front];
}
bool empty() { return _size == 0; }
int size() { return _size; }
public:
list<T> _container;
int _front = 0;
int _back = 0;
int _size = 0;
};'자료구조와 알고리즘 > 선형 자료구조 & 그래프' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2-1. 그래프 기초 (0) | 2023.07.06 |
|---|---|
| 1-8. 오른손 법칙 개선하기 (0) | 2023.07.04 |
| 1-5. 이중 배열 리스트(List) - 구현 복습 (0) | 2023.06.30 |
| 1-4. 동적 배열(vector) - 구현 복습 (0) | 2023.06.29 |
| 1-3. 배열(array), 동적 배열(vector), 연결 리스트(list) - 복습 (0) | 2023.06.29 |

